
This page shows how to use /proc/cpuinfo file and lscpu command to display number of processors on Linux. You can view /proc/cpuinfo with the help of cat command or grep command / egrep command. Model name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-3470 CPU 3. The /proc/cpuinfo file stores CPU and system architecture dependent items, for each supported architecture. For example, the /proc/uptime file gives you. Again, I'm not stating that other files don't have value, but these are the ones I've found that have the most value to me. And the most valuable of those are cpuinfo and meminfo. Model name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-3470 CPU 3.20GHzįlags : fpu de tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic mca cmov pat clflush acpi mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht nx constant_tsc nonstop_tsc pni pclmulqdq est ssse3 sse4_1 sse4_2 popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes f16c rdrand hypervisor ida arat epb pln pts dtherm fsgsbase ermsĪddress sizes : 36 bits physical, 48 bits virtual The /proc files I find most valuable, especially for inherited system discovery, are: cmdline. According to my cpuinfo I can't because vmx flag is not preset. cat /proc/cpuinfo processor : 0 vendorid : GenuineIntel cpu family : 6 model : 142 model name : Intel (R) Core (TM) i5-7360U CPU 2.30GHz stepping : 9 cpu MHz : 2303. Also before I use virtualization with vmware. flags – Defines a number of different processor attributes, such as the presence of a floating-point unit (FPU) and the ability to process MMX instructions.VT-d and VTx is enabled on BIOS but according to flags is not.Dump the flags which denote we have detected and/or have applied bug workarounds to the CPU were executing on, in a similar manner to the feature flags.

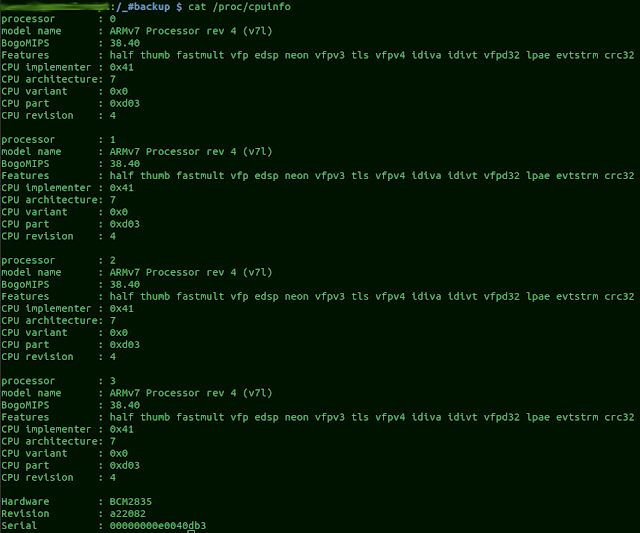
rootraspberrypi:/home/pi cat /proc/cpuinfo processor : 0 model name : ARMv7 Processor rev 3 (v7l) BogoMIPS : 108. The intent of the bugs field in /proc/cpuinfo is described in the commit message which introduced it: x86/cpufeature: Add bug flags to /proc/cpuinfo. It can easily be read with a command such as cat, i.e., cat /proc/cpuinfo If a computer contains two or more CPUs, the information about each is separated by a blank line. cache size – Tells you the amount of level 2 memory cache available to the processor. My 4GB model returns a different revision. /proc/cpuinfo is a short, read-only, plain text file that contains information about the CPUs (central processing units) on a computer.cpu MHz – Shows the processor’s precise speed, in megahertz, to the thousandth decimal point.model name – Gives you the common name of the processor, including the project name.This is helpful to determine the type of architecture of an older system and is helpful in determining which compiled RPM package would best suit that system. If your computer is an Intel-based system, simply place the number in front of “86” to determine the value. cpu family – Authoritatively tells you the type of processor you have in the system.The following is an example of the output typical of /proc/cpuinfo. The lscpu command gathers the CPU details such as number of CPUs, threads, cores, sockets, and Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) nodes. If you have more than one processor it will display all processor information separately counting the processors using zero notation. This virtual file identifies the type of processor used by your system. Method 1- Check CPU information using lscpu The lscpu command line utility collects CPU architecture information from sysfs and architecture-specific libraries like /proc/cpuinfo. If you have one processor it will display a 0. The file /proc/cpuinfo displays what type of processor your system is running including the number of CPUs present. processor – Provides each processor with an identifying number.Open your terminal and use less or cat to display the contents of /proc/cpuinfo: less /proc/cpuinfo The command will print each logical CPU with an identifying number. It will work no matter what Linux distribution you are using.
You can easily read its content and display it to the terminal on standard output by using the cat command. Model name : Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2660 0 2.20GHzįlags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush dts acpi mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht tm pbe syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon pebs bts rep_good xtopology nonstop_tsc aperfmperf pni pclmulqdq dtes64 monitor ds_cpl vmx smx est tm2 ssse3 cx16 xtpr pdcm pcid dca sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx lahf_lm ida arat epb pln pts dtherm tpr_shadow vnmi flexpriority ept vpid xsaveoptĪddress sizes : 46 bits physical, 48 bits virtualīelow is the various items you would see in the output and their respective explanations. Identifying the type of processor using the proc/cpuinfo file does not require installing any additional programs. The /proc/cpuinfo is a read-only file that contains information about the central processing units on a machine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
